Implicit differentiation is a core calculus concept used to find the derivative of an equation where a function is not written explicitly in terms of x. Instead of isolating a single variable, you differentiate both sides of the equation and apply key rules such as the chain rule and product rule to compute the correct derivative. This approach is especially useful when dealing with an implicit function that cannot be easily rewritten, making it an essential skill in higher-level math.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to solve implicit differentiation problems step by step, from identifying the correct rule to simplifying the final solution. Each step will show how to calculate and simplify expressions clearly so you can confidently find the correct answer.
In high school physics, students often start with the kinematics equation set, which works under one key condition: constant acceleration. These equations connect variables like initial velocity, final velocity, time, and position. Whether it’s rotational motion or straight-line movement, they give us a mathematical, often algebra-based way to understand both linear and rotational motion using vectors and scalars.
How to Do Implicit Differentiation Step by Step
Implicit differentiation follows a clear algebraic process. While the idea may feel unfamiliar at first, breaking it down into steps makes the method much easier to apply and understand. Below is a structured explanation that shows how derivatives of implicit functions are found in practice.
Step 1: Differentiate Both Sides of the Equation
Begin by differentiating every term in the equation with respect to 𝑥. At this stage, treat y as a function of 𝑥, not as an independent constant. This means that when you take the derivative of any term containing 𝑦, you must remember that 𝑦 changes as 𝑥 changes. Standard rules from calculus apply here, including the power rule, quotient rule, and other differentiation techniques, depending on the form of the equation.
Step 2: Apply the Chain Rule When Differentiating 𝑦
Whenever a term includes 𝑦, the chain rule must be used. This is why 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 appears in your work, it represents the rate of change of y with respect to 𝑥. Applying the chain rule correctly is essential for finding accurate derivatives of implicit functions.
Step 3: Collect All d𝑦/d𝑥 Terms
After differentiating, group all terms containing 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 on one side of the equation. This step relies on careful algebra and is where small errors often occur, so work slowly and show each step in detail.
Step 4: Factor and Solve for the Derivative
Factor out 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥, then isolate it to obtain the final derivative. This completes the step-by-step solution. To check your work, you may use an online implicit tool. An implicit differentiation calculator will find the same result when you enter the equation and press the calculation button. However, calculators should be used to verify answers, not replace understanding, as relying on them alone can hide mistakes or input error. For accurate solutions, mastering the process is key.
Example 1 (Basic Implicit Differentiation Problem)
Problem:
Differentiate the implicit function
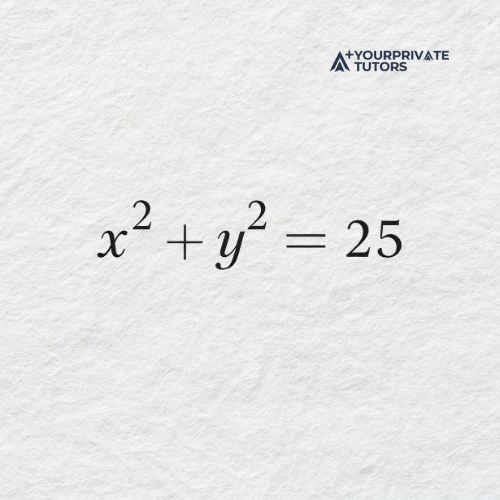
This is a simple implicit equation involving both 𝑥 and 𝑦, where the function is not written explicitly in terms of one variable.
Step-by-step explanation:
Differentiate both sides of the equation with respect to
𝑥. The derivative of 𝑥² is 2𝑥. When differentiating 𝑦 ², remember that 𝑦 is a function of 𝑥, so the chain rule applies. This gives 2𝑦 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥. The derivative of the constant 25 is zero.
After differentiation, the equation becomes:
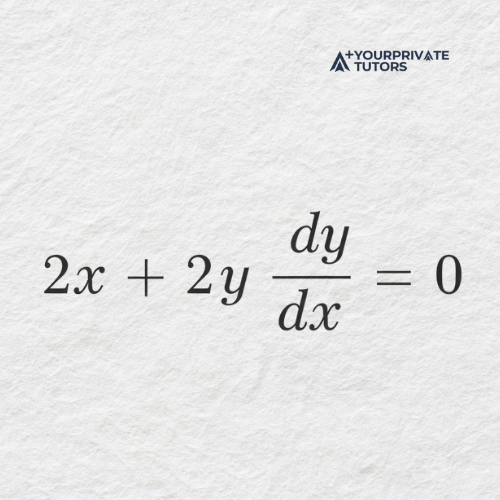
Next, isolate the term containing 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 and solve algebraically:
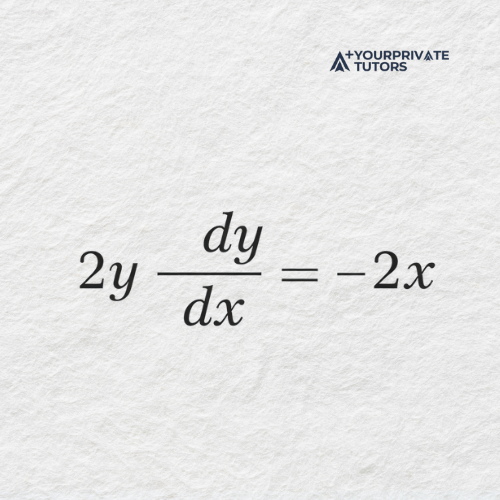
Divide both sides by 2𝑦:
Final answer:
The derivative of the implicit function is
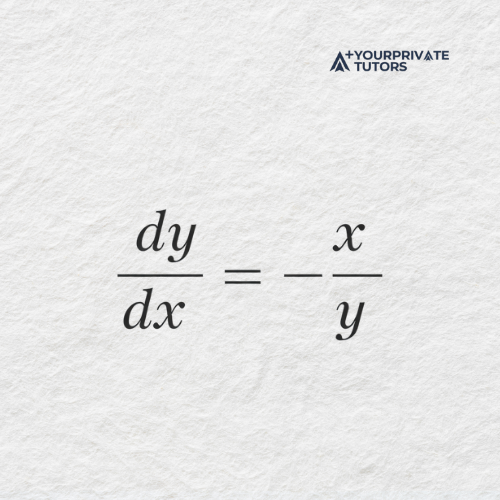
This result shows how the rate of change of 𝑦 depends on both variables.
Make Implicit Differentiation Click
Break down implicit differentiation into simple steps, understand why each step works, and solve problems with confidence.
Example 2 (Solving an Implicit Differentiation Problem Using the Product Rule)
Problem:
Differentiate the equation
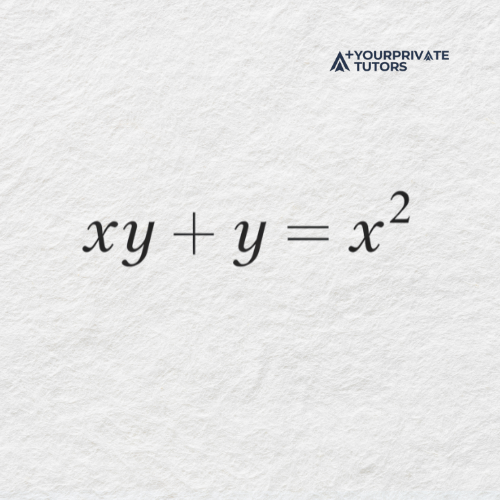
This example is more advanced because it requires both the product rule and the chain rule, making it a common source of confusion for students.
Step-by-step explanation:
Differentiate each term with respect to 𝑥. For the term 𝑥𝑦, apply the product rule:
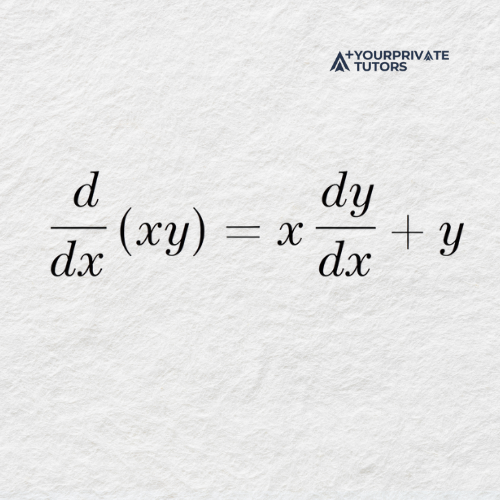
The derivative of 𝑦 is 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥, and the derivative of 𝑥² is 2𝑥. Putting this together:

Now collect all terms containing 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 on one side:
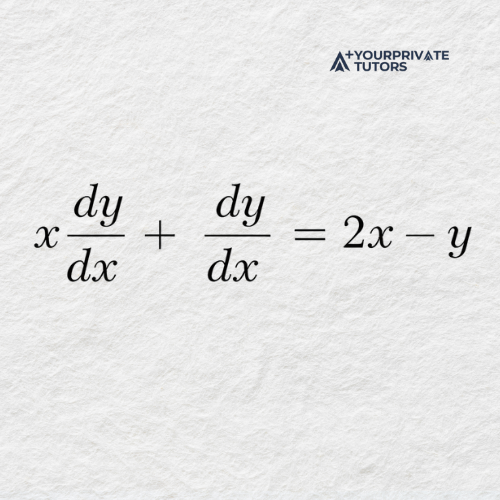
Factor out 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥.
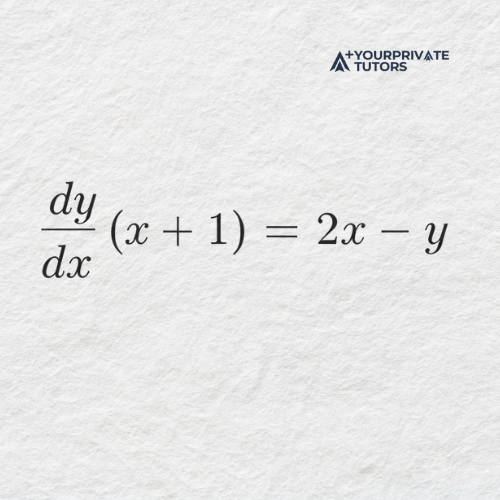
Finally, solve for the derivative:
Final answer:
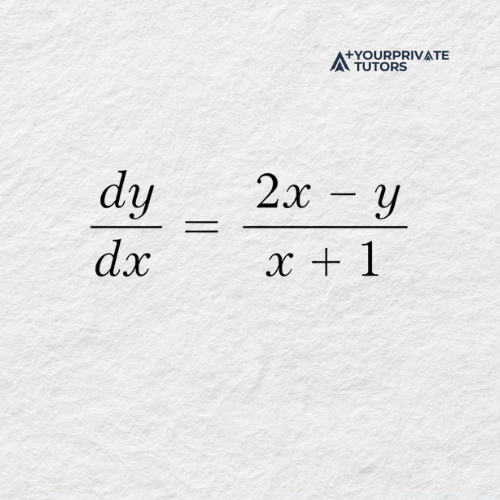
This example highlights how implicit differentiation handles products and reinforces the importance of careful algebra at each step.
Solving Implicit Differentiation Problems Using a Calculator
Calculators can be helpful learning tools when working with implicit differentiation, especially after you understand the manual process. An implicit differentiation calculator or implicit derivative calculator allows you to verify results and catch algebra mistakes, but it should not replace learning the steps. To begin, you simply input the implicit function like for example, an equation involving both 𝑥 and 𝑦 into an online calculator or math solver. After clicking the calculate or solve button, the tool returns the derivative, often written as an implicit derivative.
Some tools function as a calculator with steps, showing a step-by-step breakdown of the differentiation process. This output explains how implicit derivatives are formed and how terms are simplified, helping you understand the logic behind the solution. Using a derivative calculator correctly reinforces learning, but true mastery comes from knowing how to solve implicit differentiation problems by hand before relying on automated calculation.
Practice Tips to Solve Implicit Differentiation Problems Faster
Improving speed and accuracy with implicit differentiation comes from developing strong habits, not relying on shortcuts. Before you begin any calculation, rewrite the function clearly so every term involving 𝑥 and 𝑦 is easy to identify. Many students find it helpful to circle or underline all 𝑦 terms to remember where implicit derivatives will appear. Working step by step reduces errors and makes the final solution easier to verify.
After solving a problem manually, you can check your answer using a derivative calculator or implicit derivative calculator as a confirmation tool. An online calculator can quickly compute results from your input, but understanding each step ensures you can spot mistakes and explain your reasoning. With consistent practice, using implicit differentiation becomes more intuitive and efficient.
Final Thoughts on Using Implicit Differentiation Effectively
Mastering implicit differentiation is about understanding the process, not memorizing formulas or depending entirely on a calculator. While tools like an implicit differentiation calculator or calculator with steps can help verify results, they should support not replace your grasp of the underlying calculus concepts.
Being able to solve for an implicit function by hand strengthens your understanding of implicit derivatives and prepares you for more advanced applications. In real-world contexts, especially in science and engineering, accuracy matters, and knowing how each step leads to the final solution is essential.
With clear explanations, careful practice, and the right guidance, using implicit differentiation becomes a skill you can apply confidently across a wide range of problems.



